Duke Univeristy | Duke Medicine | School of Medicine | School of Nursing | Doctor of Physical Therapy
Copyright © 2004-2010 Duke University School of Medicine
Anatomy Tables - Pectoral Region, Posterior Shoulder & Breast |
|||||
Osteology |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | Structure | Description | Notes |
| os coxae (TG6-3) | one of three bones that form the pelvis | paired; the os coxae forms the lateral part of the pelvis; it is formed by three fused bones: ischium, ilium & pubis; also known as the innominate bone (Latin, os = bone) | |
| pubis (TG6-4) | an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis | one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its body forms 1/5 of the acetabulum; its symphyseal surface unites with the pubis of the opposite side to form the pubic symphysis; the superior and inferior pubic rami participate in the formation of the obturator foramen | |
| pubic crest | ridge on the superior border of the superior ramus | attachment of rectus abdominis & pyramidalis mm. | |
| pubic tubercle | process at the lateral end of pubic crest | attachment point of the medial end of the inguinal ligament | |
| pecten | ridge on superior surface of the superior pubic ramus | attachment point of the pectineal ligament | |
| ilium (TG6-3) | fan-shaped bone that forms the lateral prominence of the pelvis | one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis | |
| iliac crest | arching superior edge of the ilium that forms the rim of the "fan" | attachment for abdominal wall muscles | |
| iliac tubercle | roughened area along the outer edge of the iliac crest | ||
| anterior superior iliac spine | spine at the anterior end of the iliac crest | lateral attachment of the inguinal ligament | |
| arcuate line | ridge running from anteroinferior to posterosuperior on the inner surface of the ilium | inferior boundary of the iliac fossa; marks the plane of transition from abdominal cavity to pelvic cavity; part of the iliopectineal line (Note: this is obviously not the same arcuate line as is found on the posterior aspect of the rectus sheath) (Latin, arcuate = bowed) | |
Muscles |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation | Artery | Notes | Image |
| external abdominal oblique (N249, TG5-04) | lower 8 ribs | linea alba, pubic crest & tubercle, anterior superior iliac spine & anterior half of iliac crest | flexes and laterally bends the trunk | intercostal nerves 7-11, subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves | musculophrenic a., superior epigastric a., intercostal aa. 7-11, subcostal a., lumbar aa., superficial circumflex iliac a., deep circumflex iliac a., superficial epigastric a., inferior epigastric a., superficial external pudendal a. | the inguinal ligament is a specialization of the external abdominal oblique aponeurosis; the external spermatic fascia is the external abdominal oblique muscle's contribution to the coverings of the testis and spermatic cord |  |
| internal abdominal oblique (N250, TG5-04) | thoracolumbar fascia, anterior 2/3 of the iliac crest, lateral 2/3 of the inguinal ligament | lower 3 or 4 ribs, linea alba, pubic crest and pecten | flexes and laterally bends the trunk | intercostal nerves 7-11, subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves | musculophrenic a., superior epigastric a., intercostal aa. 7-11, subcostal a., lumbar aa., superficial circumflex iliac a., deep circumflex iliac a., superficial epigastric a., inferior epigastric a., superficial external pudendal a. | anterior fibers of internal abdominal oblique course up and medially, perpendicular to the fibers of external abdominal oblique; the cremaster muscle and fascia is the internal abdominal oblique muscle's contribution to the coverings of the testis and spermatic cord | 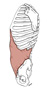 |
| transversus abdominis (N251, TG5-05) | lower 6 ribs, thoracolumbar fascia, anterior 3/4 of the iliac crest, lateral 1/3 of inguinal ligament | linea alba, pubic crest and pecten | flexes and laterally bends trunk | intercostal nerves 7-11, subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves | musculophrenic a., superior epigastric a., intercostal aa. 7-11, subcostal a., lumbar aa., superficial circumflex iliac a., deep circumflex iliac a., superficial epigastric a., inferior epigastric a., superficial external pudendal a. | transversus abdominis muscle does not contribute to the coverings of the spermatic cord and testis; transversalis fascia, the deep fascia that covers the inner surface of the transversus abdominis, forms the internal spermatic fascia | 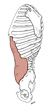 |
| rectus abdominis (N250, TG5-05) | pubic crest and symphysis | xiphoid process of the sternum and costal cartilages 5-7 | flexes the trunk | intercostal nerves 7-11 and subcostal nerve | superior epigastric a. intercostal aa., subcostal a., inferior epigastric a. | rectus sheath contains rectus abdominis and is formed by the aponeuroses of external and internal oblique and transversus abdominis mm. (Latin, rectus = straight) | 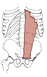 |
| pyramidalis (TG5-10) | pubic crest, anterior to rectus abdominis | linea alba | draws the linea alba inferiorly | subcostal nerve | subcostal a., inferior epigastric a. | the pyramidalis m. is not always present | 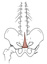 |
| cremaster (TG5-04) | inguinal ligament | forms thin network of muscle fascicles around the spermatic cord and testis (or around the distal portion of the round ligament of the uterus) | elevates testis (not well developed in females) | genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve | cremasteric a., a branch of the inferior epigastric a. | the cremaster m. is internal abdominal oblique muscle's contribution to the coverings of the spermatic cord and testis; the cremasteric reflex may be elicited by stroking the medial thigh (where the femoral branch of the genitofemoral n. distributes cutaneously) (Greek, cremaster = a suspender) | 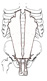 |
Joints and Ligaments |
||
|---|---|---|
| Joint | Description | Significance |
| linea alba (N249,N251,N252A,N252B, TG5-05, TG5-06) | connects xiphoid with pubic symphysis & crest | formed by intermingling of aponeuroses of external abdominal oblique, internal abdominal oblique, & transversus abdominis (Latin, linea alba = white line) |
| inguinal ligament (N250,N251, TG5-04) | the ligament that connects the anterior superior iliac spine with the pubic tubercle | the inguinal ligament is a specialization of the inferior border of the external abdominal oblique aponeurosis; it is the site of origin for a part of the internal abdominal oblique muscle and for a part of the transversus abdominis muscle; also known as: Poupart's ligament |
| lacunar ligament (N251,N262, TG5-08D, TG5-09D) | an extension of the medial end of inguinal ligament which connects the pubic tubercle with the pecten of the pubis | the lacunar ligament is a flattened portion of the aponeurosis of the external abdominal oblique m. that projects posteriorly from the pubic tubercle; it forms the medial border of the femoral ring and the floor of the inguinal canal at the superficial inguinal ring (Latin, lacuna = a lake or pit) |
| pectineal ligament (N251,N262, TG5-08D, TG5-09D) | a thickening of fascia on the pecten of the pubis | the pectineal ligament looks like an extension of the lacunar ligament along the surface of the pectineal line; also known as Cooper's ligament (note: Cooper's ligaments are also found in the breast) |
| pubic symphysis (TG6-04) | symphysis | midline joint uniting the pubic bodies (Greek, symphysis = a growing together) |
| falx inguinalis | the inferomedial attachment of internal abdominal oblique and transversus abdominis | also known as: conjoint tendon (Latin, falx = sickle) |
Nerves |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nerve | Source | Branches | Motor | Sensory | Notes |
| intercostal n. (N254,N257, TG5-02) | ventral primary rami of spinal nerves T1-T11 | lateral & anterior cutaneous brs. | intercostal muscles; abdominal wall muscles (via T7-T11); muscles of the forearm and hand (via T1) | skin of the chest and abdomen anterolaterally; skin of the medial side of the upper limb (via T1-T2) | intercostal n.travels below the posterior intercostal a. in the costal groove |
| subcostal n. (N254,N257, TG5-02) | ventral primary ramus of T12 | lateral cutaneous br., anterior cutaneous br. | muscles of the abdominal wall | skin of the anterolateral abdominal wall | the subcostal n. is equivalent to a posterior intercostal n. found at higher thoracic levels |
| iliohypogastric n. (N257,N266, TG5-02, TG5-38) | lumbar plexus (ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve L1) | lateral and anterior cutaneous brs. | muscles of the lower abdominal wall | skin of the lower abdominal wall, upper hip and upper thigh | iliohypogastric n. receives a contribution from T12 in approximately 50% of cases |
| ilioinguinal n. (N257,N266, TG5-02, TG5-38) | lumbar plexus (ventral primary ramus of spinal nerve L1) | anterior cutaneous br. (also known as: anterior labial/scrotal n.) | muscles of the lower abdominal wall | skin of the lower abdominal wall and anterior scrotum/labium majus | ilioinguinal n. courses through the inguinal canal and superficial inguinal ring |
| genitofemoral (TG5-02) | lumbar plexus (ventral primary rami of L1-L2) | genital & femoral brs. | cremaster m. | skin of anterior scrotum/labia majora & upper medial thigh | lies on psoas major in abdomen; genital br. passes through deep inguinal ring & inguinal canal; brushing thigh elicits elevation of testis via cremasteric reflex |
Arteries |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artery | Source | Branches | Supply to | Notes |
| epigastric, inferior (N25,N253, TG5-05, TG5-07) | external iliac a. | cremasteric a. | lower rectus abdominis m., pyramidalis m., lower abdominal wall | inferior epigastric a. anastomoses with the superior epigastric a. within the rectus abdominis m. |
| epigastric, superficial (N249, TG5-02) | femoral a. | cutaneous brs. | superficial fascia and skin of the lower abdominal wall | superficial epigastric a. is one of three superficial arteries that arise from the femoral a. (see also: superficial circumflex iliac a. and superficial external pudendal a.) |
| epigastric, superior (N191, TG4-08, TG5-05) | internal thoracic a. | no named branches | upper rectus abdominis m., upper abdominal wall | superior epigastric a. is the direct continuation of the internal thoracic a.; it anastomoses with the inferior epigastric a. within the rectus abdominis m. |
| intercostal, posterior (TG4-39) | highest intercostal (upper 2 intercostal spaces), descending thoracic aorta (3rd-11th intercostal spaces) | posterior br., spinal br., anterior br., collateral br., lateral cutaneous br. | intercostal muscles, spinal cord and vertebral column, deep back muscles, skin and superficial fascia overlying the intercostal spaces | posterior intercostal aa. supply the lateral and posterior portions of the intercostal space; anterior intercostal aa. supply the anterior portions of the intercostal spaces |
| subcostal (TG4-39) | descending thoracic aorta | spinal br., collateral br., lateral cutaneous br. | vertebrae, spinal cord; muscles, skin & fascia of the upper abdominal wall | subcostal a. is equivalent to a posterior intercostal a., but is named subcostal because it courses inferior to the 12th rib |
Topographic Anatomy |
||
|---|---|---|
| Structure/Space | Description/Boundaries | Significance |
| arcuate line (TG5-05, TG5-07) | anatomical feature on the inner surface of the abdominal wall; a fascial line in the transverse plane approximately 1/2 of the distance from the umbilicus to the pubic symphysis | arcuate line is the point at which the posterior lamina of the rectus sheath ends and transversalis fascia lines the inner surface of the rectus abdominis m. (Latin, arcuate = bowed) |
| epigastric region (TG5-01) | an area on the anterior abdominal wall between the midclavicular lines, superior to the transpyloric line | one of 9 regions of the abdomen |
| hypochondriac region (TG5-01) | an area on the anterior abdominal wall lateral to the midclavicular line, superior to the transpyloric line | right and left hypochondriac regions comprise 2 of 9 regions of the abdomen |
| hypogastric region (TG5-01) | an area on the anterior abdominal wall between the midclavicular lines, inferior to the intertubercular line | one of 9 regions of the abdomen; also known as: pubic region |
| inguinal region (TG5-01) | anterior abdominal wall lateral to midclavicular line, inferior to intertubercular line | right and left inguinal regions comprise 2 of 9 regions of the abdomen; also known as: iliac region |
| intercristal line | an imaginary line drawn in the horizontal plane at the upper margin of the iliac crests | intercristal line locates the level of the L4 vertebra; a useful landmark in spinal tap procedure |
| intertubercular line (TG5-01) | an imaginary line drawn in the horizontal plane at the upper margin of the iliac tubercles | intertubercular line locates the level of the L5 vertebra; used with midinguinal and transpyloric lines to divide the abdominal wall into 9 regions |
| linea alba (N249,N251,N252A,N252B, TG5-05, TG5-06) | anatomical feature on the midline of the anterior abdominal wall; an aponeurotic band that extends from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis; | linea alba is formed by the combined abdominal muscle aponeuroses; it is used for midline abdominal incisions to avoid major nerves or vessels (Latin, linea alba = white line) |
| lumbar region | an area on the anterior abdominal wall lateral to the midclavicular line, inferior to transpyloric line, superior to intertubercular line | right and left lumbar regions comprise 2 of 9 regions of the abdomen; also known as: lateral region |
| McBurney's point (TG5-15) | a point on the anterior abdominal wall which is 1/3 of the distance along a line from the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus | McBurney's point is the approximate location of the vermiform appendix; point of tenderness in appendicitis |
| midaxillary line (TG4-01) | an imaginary vertical line passing through the middle of the axilla | used as a surface landmark for descriptive purposes |
| midclavicular line (TG4-01) | an imaginary vertical line passing through the midshaft of the clavicle | used as a surface landmark for descriptive purposes |
| midinguinal line (TG5-01) | an imaginary vertical line passing through the midpoint of inguinal ligament | used with the transpyloric and intertubercular lines to divide the abdomen into 9 regions |
| quadrant, inferior left (TG5-01) | a region on the anterior abdominal wall defined by the midline and the transumbilical line | one of 4 abdominal quadrants |
| quadrant, inferior right (TG5-01) | a region on the anterior abdominal wall defined by the midline and the transumbilical line | one of 4 abdominal quadrants |
| quadrant, superior left (TG5-01) | a region on the anterior abdominal wall defined by the midline and the transumbilical line | one of 4 abdominal quadrants |
| quadrant, superior right (TG5-01) | a region on the anterior abdominal wall defined by the midline and the transumbilical line | one of 4 abdominal quadrants |
| semilunar line (TG5-01) | an anatomical feature of the anterior abdominal wall; the lateral edge of the rectus abdominis m. | semilunar line is formed by the fused aponeuroses of the abdominal wall mm. at the lateral margin of the rectus sheath |
| transpyloric line (TG5-01) | an imaginary horizontal line 1/2 of the distance between the jugular notch and the pubic crest | transpyloric line is used with the midinguinal and intertubercular lines to divide the abdominal wall into 9 regions; the fundus of the gall bladder lies at the intersection of the transpyloric line with the right 9th costal cartilage; the pylorus of the stomach is located at this plane; a horizontal plane through the transpyloric line locates the level of the L1 vertebra |
| transumbilical line (TG5-01) | an imaginary horizontal line through the umbilicus | transumbilical line is used with the midline to divide abdomen into 4 quadrants |
| transverse lines | anatomical features in the anterior abdominal wall; folds in the anterior abdominal wall (usually 3) | transverse lines are creases that overlie the tendinous intersections in the rectus abdominis m. |
| umbilical region | a region on the anterior abdominal wall between the midclavicular lines, inferior to the transpyloric line, superior to the intertubercular line | one of 9 regions of the abdomen |
| umbilicus (TG5-01) | remnant of the attachment of the umbilical cord to the anterior abdominal wall | umbilicus marks the approximate level of the L3/L4 intervertebral disc in non-obese individuals (Latin, umbilicus = navel) |
| superficial (external) inguinal ring (N387,N249,N259,N260, TG5-08A, TG5-09A) | slitlike opening between the diagonal fibers of the aponeurosis of the external oblique, superolateral to the pubic tubercle | exit from the inguinal canal |
| deep (internal) inguinal ring (TG5-08C, TG5-09C) | site of an outpouching of the transversalis fascia approx. 1.25 cm superior to the middle of the inguinal ligament and lateral to the inferior epigastric a. | opening into the inguinal canal |
| inguinal canal (N387,N249,N259,N260, TG5-08A, TG5-09A) | Anterior - aponeurosis of the ext. oblique; Posterior - transversalis fascia; Roof - fibers of the int. oblique and transverse abdominis; Floor - superior surface of the inguinal ligament | pathway for the spermatic cord in males and round ligament of the uterus in females |
Viscera/Fascia |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | Location | Description | Notes |
| thoracolumbar aponeurosis (fascia) (N174, TG1-13) | extends laterally from the spinous processes and forms a thin covering for the deep muscles in the thoracic region and a strong, thick covering for muscles in the lumbar region | forms the aponeurotic origin of latissimus dorsi | (Greek, aponeurosis = a broad, flat nerve; due to the resemblance between nerves & tendons) |
| conjoint tendon (TG5-08D, TG5-09D) | attached to pubic crest and pecten pubis | the most inferior, medial tendinous fibers of the internal oblique join with the aponeurotic fibers of the deeper transverse abdominis | also called the falx Inguinalis |
| ductus deferens (TG5-08D, TG5-09D) | passes through superficial inguinal ring, inguinal canal & deep ring to reach posteroinferior surface of bladder where it joins with duct of seminal vesicle to form ejaculatory duct | continuous with tail of epididymis | (Latin, ductus = to lead + deferens = to carry away) |
| fascia, cremasteric (TG5-08B, TG5-09B) | intermediate covering of spermatic cord | derived from internal abdominal oblique muscle (Greek, fascia = a band + cremaster = a suspender) | |
| fascia, external spermatic (TG5-08B, TG5-09B) | outermost covering of spermatic cord | derived from aponeurosis of external abdominal oblique muscle (Greek fascia = a band) | |
| fascia, internal spermatic (TG5-08C, TG5-09C) | innermost covering of spermatic cord | derived from transversalis fascia | |
| fascia lata (N249, TG3-02) | deep fascia forming tubular investment of the thigh | thickened laterally as iliotibial tract/band; connected to femur by lateral & medial intermuscular septa | Scarpa's fascia attaches to it below inguinal ligament |
| crus, lateral (TG5-08C, TG5-09C) | lateral border of superficial inguinal ring | attaches to pubic tubercle | (Latin, crus = leg) |
| crus, medial (TG5-08C, TG5-09C) | medial border of superficial inguinal ring | attaches to pubic crest | (Latin, crus = leg) |
| rectus sheath (N249,N251,N252A,N252B, TG5-05, TG5-06, TG5-06) | tough, aponeurotic, tendinous sheath of the rectus abdominis muscle | (Latin, rectus = straight) | |
| round ligament of uterus (N397, TG5-09A, TG5-09C, TG5-09D) | attaches to inner aspect of labia majora, traverses superficial inguinal ring, inguinal canal & deep inguinal ring to reach lateral surface of uterus below uterine tube | continuous with ovarian ligament | a.k.a. ligamentum teres uteri; remnant of gubernaculum (Latin, teres = round) |
| scrotal ligament (TG6-31A) | band of connective tissue that attaches the inferior end of the testis to the inner aspect of the scrotal sac | scrotal ligament is the remnant of the gubernaculum testis | |
| scrotum (TG6-31A) | sac of hair-covered skin containing the testis | in the scrotum the fatty and membranous layers of the superficial fascia (as seen in the lower abdominal wall) are fused to form the tunica dartos scroti | |
| spermatic cord (N387, TG5-08A, TG5-08C, TG5-08D, TG5-10C) | bundle of vessels, nerves and lymphatics ensheathed in tissue layers derived from the abdominal wall; it begins at the deep inguinal ring, passes through the inguinal canal and the superficial ring to reach the testis in the scrotum | spermatic cord comprises the: ductus deferens, testicular a., pampiniform plexus, deferential a. & v. and genital br. of the genitofemoral n.; coverings of the cord are the: internal spermatic fascia (from the transversalis fascia), cremasteric muscle and fascia (from the internal abdominal oblique), external spermatic fascia (from the external abdominal oblique aponeurosis) | |
| testis (TG6-32B) | an endocrine and exocrine gland contained within the scrotum | testis is the male gonad; its exocrine product is sperm which drain to the head of the epididymis via efferent ductules; its endocrine product is testosterone; the testis migrates into the scrotum shortly before birth; it is tethered to the scrotum inferiorly by the scrotal ligament (a remnant of the gubernaculum) | |
| tunica dartos scroti (TG6-32B) | a subcutaneous layer of smooth muscle located in the scrotum | fatty and membranous layers of the superficial fascia (as seen in the lower abdominal wall) are fused in the scrotum to form the tunica dartos scroti | (Greek, dartos = leather) |
| tunica vaginalis testis (TG6-32B) | a peritoneal sac located anterolateral to the testis | tunica vaginalis testis has two layers: visceral and parietal; the visceral layer lies on the anterolateral surface of the testis and epididymis; the parietal layer lines the inner surface of the scrotal sac | (Latin, vagina = sheath) |
| fascia, transversalis (N251,N252,N259, TG5-07) | lines majority of abdominal wall | covers the deep surface of the transverse abdominis and its aponeurosis | right and left sides continuous deep to the linea alba |
| fascia, weak (N251,N252,N259, TG5-07) | located in the inguinal triangle | hernias can occur here | |
Lymphatics |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Location | Afferents from | Efferents to | Regions drained | Notes |
| superficial inguinal nodes (TG6-34) | in the superficial fascia parallel to the inguinal ligament and along the terminal part of the greater saphenous v. | lymphatic vessels from the superficial lower limb, superficial abdominal wall, perineum | external iliac nodes; deep inguinal nodes | lower abdominal wall; external genitalia; superficial parts of the lower limb | superficial inguinal nodes are 12-20 in number; they become inflamed during infections of the lower limb; they may become inflamed during infections of the external genitalia |
Click here to submit questions or comments about this site. Updated 09/26/11 - Velkey |